Measles
Last update: 2024-05-23
What’s on this page:
Key facts
Transmission: Airborne and direct contact
- When infected people cough, sneeze, blow their nose or spit, they spread small particles through the air, which are then breathed in by other people
- Direct contact (for example, through kissing, sharing cups or eating utensils) with infected saliva or nose mucous
Most vulnerable to severe consequences
- Children under the age of five years
- Especially children suffering from malnutrition
- Unvaccinated pregnant women
- Unvaccinated adults over the age of 30
- People who have weakened immune systems (for example, people living with HIV/AIDS)
Most vulnerable to contracting the disease
- ** Any unvaccinated person is at risk of getting and transmitting measles, but the risk of outbreak is greater when people live in cramped or overcrowded conditions, such as people living in shelters or refugee camps
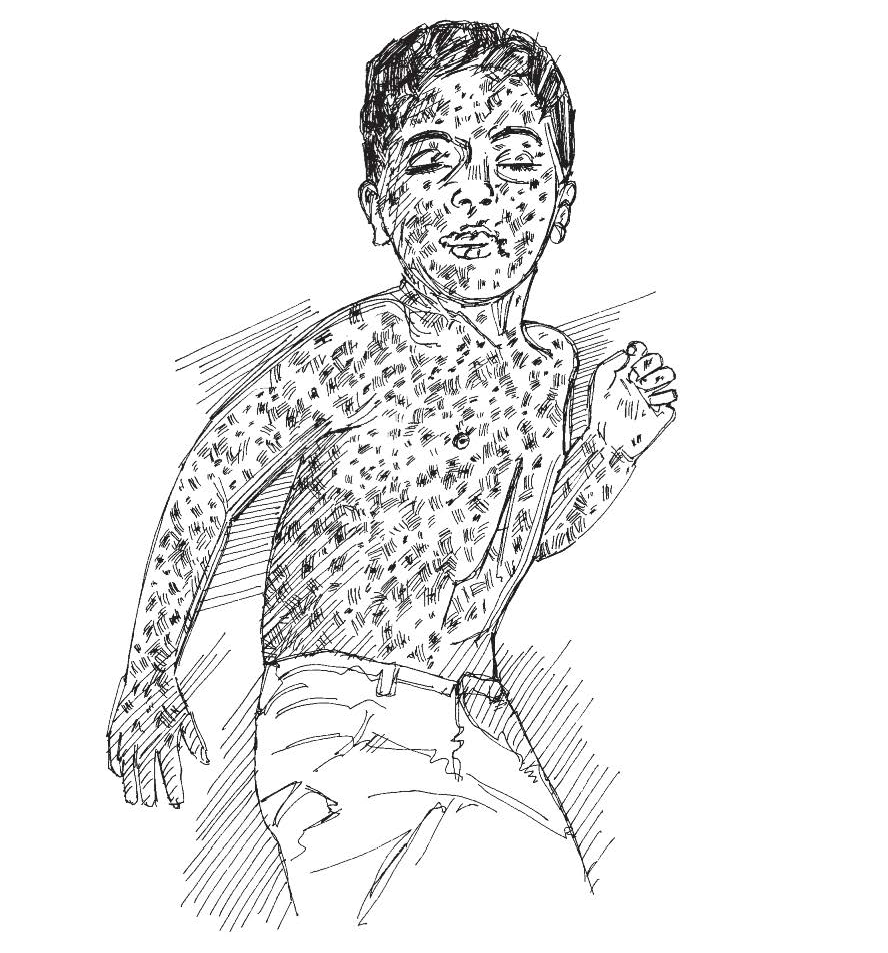
Symptoms
- High fever
- Flat, red, blotchy rash - starting on the head, face and neck, and then spreading to the rest of the body (usually starts a few days after the fever begins)
- Runny nose (sometimes)
- Cough (sometimes)
- Red and watery eyes (sometimes)
- Small white spots inside the mouth (sometimes)
- Diarrhoea (sometimes)
What can you do to prevent and control an epidemic?
Monitoring the community and identifying sick people
- Identify and isolate sick people before they spread the disease to others
- Sick people should be isolated from others for at least four days after they develop the red rash
Treatment and management
- Refer those with suspected measles to health facilities or measles treatment centres
- Manage and improve nutritional situation, especially of children
- Encourage exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, and complementary breastfeeding until the age of two years (especially when a child is sick).
- Check the nutritional status of children under five years (MUAC screening)
- Refer cases of suspected malnutrition to health services and support nutritional programming
- Provide psychosocial support to the sick person and their family members
Safe shelters and spaces
- Reduce overcrowding and improve ventilation in living shelters, workplaces and schools, if possible
- Hand and respiratory hygiene: Promote good hand hygiene (handwashing with soap)
- BEFORE: preparing food; eating; feeding a child; treating wounds; or caring for sick people
- AFTER: using the toilet or cleaning a baby; touching garbage or waste; touching or feeding animals; blowing nose, coughing or sneezing; treating wounds or caring for sick people
- Promote respiratory hygiene and coughing etiquette (cover cough or sneeze using a sleeve or tissue, wash hands after coughing or sneezing, do not spit onto the ground or in public)
Social mobilization and health promotion
- Find out the specific advice being given by health and other relevant authorities
- Promote recommended health practices (such as routine vaccination, social distancing, separation of healthy people and sick people, etc.)
- Model following this advice and inform community members of current health practice advice
- Offer support and encouragement to follow the advice
- Try to gain understanding about if and why health practice advice is not being followed
- With the guidance of your supervisor and health authorities, work with communities to overcome barriers to following health advice and recommended practices
Immunization
- Promote routine vaccination programmes for children
- Support mass vaccination campaigns
Mapping and community assessment
Mapping and community assessment
- Make a map of the community.
- Mark the following information on the map:
- How many people have fallen sick with measles? Where?
- How many people have died? Where? When?
- Who and where are the vulnerable people?
- Where are health facilities or measles treatment centres? (include traditional healers)
- Record the following information on the back of the map:
- When did people start to fall sick with measles?
- How many people live in the affected community? How many are children under five years?
- Are most children in the community vaccinated against measles?
- Is there a vaccination campaign planned? If so, when and where?
- Do people generally have enough food?
- How common is it for people to live together in crowded spaces? Is there ventilation and fresh air in homes, schools and workplaces?
- Apart from children, are there other groups (specific ages, occupations, geographic areas, etc.) that are badly affected?
- What are the community’s habits, practices and beliefs about vaccinations? Are there societal, cultural or religious beliefs that prevent people from getting vaccinated?
- What are the community’s habits, practices and beliefs about caring for and feeding sick people? Consider any differences in roles and responsibilities between women and men.
- When babies and infants are sick, do women continue to breastfeed them?
- Is a social mobilization or health promotion programme in place?
- Which sources do people use/trust the most for information?
- Are there rumours or misinformation about measles or vaccines? What are the rumours?
Volunteer actions
01. Community-based surveillance
02. Community mapping
03. Communicating with the community
04. Community referral to health facilities
05. Volunteer protection and safety
12. Managing fever
13. Breastfeeding
17. Measuring mid upper arm circumference (MUAC)
19. Mental Health and Psychosocial support (MHPSS)
20. Isolating sick people
24. Routine vaccinations
25. Mass vaccination campaigns
26. Respiratory hygiene and coughing etiquette
27. Shelter and ventilation
28. Physical distancing
34. Handwashing with soap
43. Social mobilization and behaviour change